Understanding Plaque Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Plaque psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin, this condition can be both physically uncomfortable and emotionally distressing. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for plaque psoriasis, providing a comprehensive understanding of this common skin disorder.
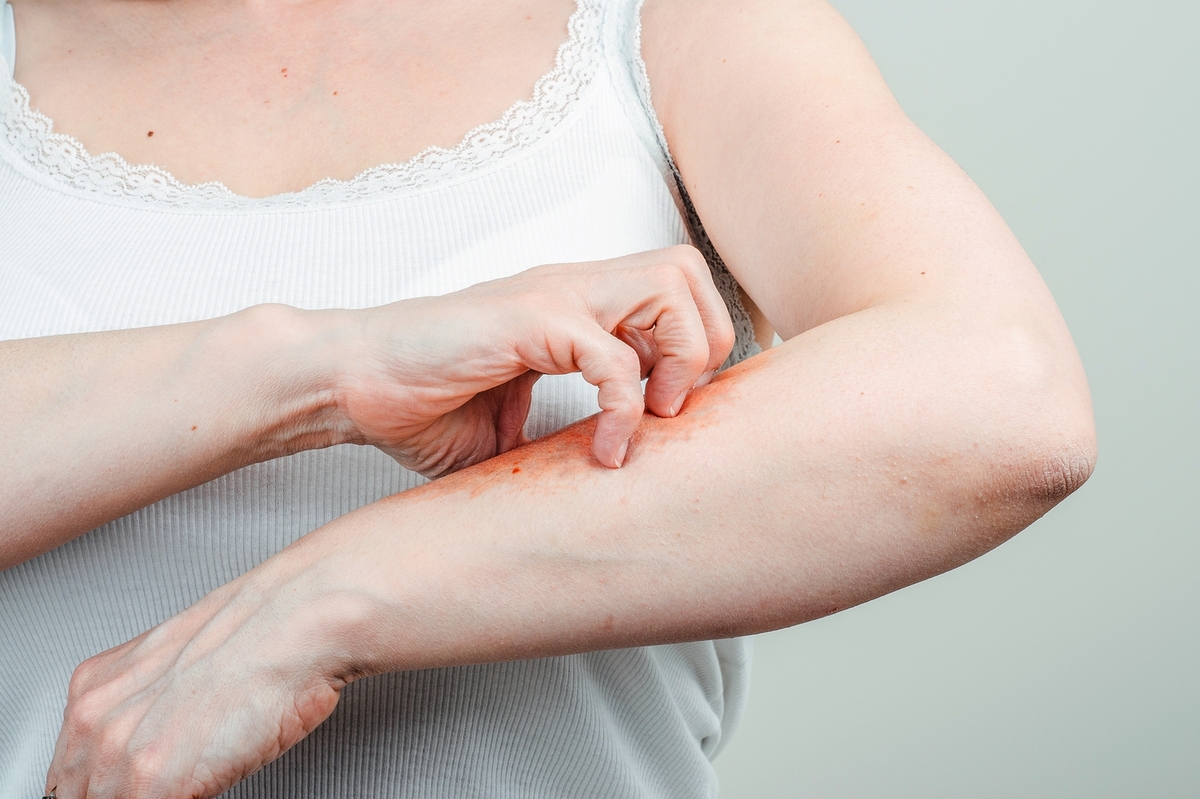
Plaque psoriasis is the most common form of psoriasis, accounting for about 80-90% of all cases. It typically presents as raised, inflamed, red lesions covered with silvery-white scales. These plaques can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. The severity of plaque psoriasis can vary greatly, with some individuals experiencing only minor irritation while others suffer from extensive and painful outbreaks.
Symptoms of Plaque Psoriasis
The primary symptoms of plaque psoriasis include:
– Red patches of skin : These patches are often covered with thick, silvery scales.
– Dry, cracked skin : The affected areas may bleed or become sore.
– Itching and burning : These sensations can range from mild to severe.
– Thickened or ridged nails : Psoriasis can also affect the nails, causing them to become thickened, pitted, or ridged.
– Swollen and stiff joints : In some cases, psoriasis is associated with psoriatic arthritis, leading to joint pain and swelling.
Causes and Triggers
The exact cause of plaque psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to an immune system malfunction. In individuals with psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to the rapid production of new skin cells. This results in the buildup of plaques on the skin’s surface.
Several factors can trigger or exacerbate plaque psoriasis, including:
– Genetics : A family history of psoriasis increases the risk of developing the condition.
– Infections : Certain infections, such as strep throat, can trigger psoriasis flare-ups.
– Stress : Emotional stress can worsen symptoms.
– Injury to the skin : Cuts, scrapes, or sunburns can trigger a psoriasis outbreak.
– Medications : Some medications, including lithium and beta-blockers, can trigger or worsen psoriasis.
– Lifestyle factors : Smoking and heavy alcohol consumption can increase the risk of psoriasis flare-ups.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for plaque psoriasis, several treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These include:
– Topical treatments : Creams and ointments containing corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, or retinoids can reduce inflammation and slow the growth of skin cells.
– Phototherapy : Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision can help reduce symptoms.
– Systemic medications : Oral or injected medications that affect the entire body can be prescribed for severe cases. These include biologics, which target specific parts of the immune system.
– Lifestyle changes : Maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress, and avoiding known triggers can help control symptoms.
Living with Plaque Psoriasis
Living with plaque psoriasis can be challenging, but with the right treatment and support, individuals can manage their symptoms effectively. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan. Additionally, joining support groups or connecting with others who have psoriasis can provide emotional support and practical advice.
Conclusion
Plaque psoriasis is a common and often distressing skin condition, but understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options can empower individuals to manage their condition effectively. By working with healthcare professionals and making lifestyle adjustments, those with plaque psoriasis can lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by this chronic condition.



